Contents
How to Fix Email Bounce Back: A Comprehensive Guide

Contents
Around 31 billion emails bounce back daily to their senders, never getting to their recipient’s inboxes.
A high email bounce back rate can seriously hurt your reputation as a sender, leading to email providers giving you a low sender score.
If your sender score is low, your emails might be automatically marked as spam, so avoiding email bounce back is critical for your email marketing strategy. Read on to understand precisely what email bounce back is and how to prevent it.
What is Email Bounce Back?
Ever sent an email that never arrived? That’s the essence of an email bounce back. Email bounce back is when emails cannot be delivered to their intended recipients.
There are numerous reasons this happens, but the sender is notified of an email bounce back via an automated message from a service provider. This message usually gives a few suggestions on how to fix the problem.
How to Identify a Bounced Email?
Identifying a bounced email is crucial in email marketing. Bounce back notifications usually land in your inbox, marked with subject lines like “Delivery Failure” or “Undelivered Mail.” These notifications typically include details about why the email bounced, helping you diagnose the issue.
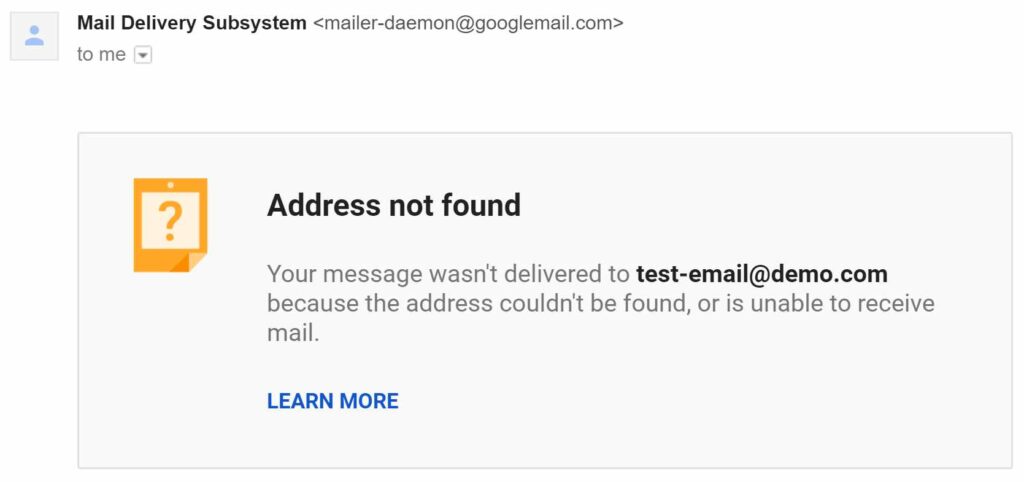
Since there are so many email service providers, there are multiple ways to be notified of an email bounce back.
The automatic reply informing you of an unsuccessful delivery can come from your email server or the intended recipient’s server.
These messages will all look similar and say, “Your email could not be delivered to example@email.com because the address couldn’t be found or is unable to receive email.” However, you can recognize and avoid emails bouncing back in many cases.
Types of Email Bounces
Not all bounces are created equal. Let’s explore the three main types:
Soft Bounce

A soft bounce occurs when the recipient’s email server temporarily cannot deliver the email. This could be due to issues like a full inbox, the recipient’s server being down, or the email being too large.
Soft bounces are usually temporary, which means they can be reattempted for a certain period before being considered a hard bounce.
Hard Bounce

A hard bounce occurs when the email is permanently rejected by the recipient’s mail server. This could happen because the email address is invalid, the domain does not exist, or the recipient’s email server has blocked the sender.
Hard bounces indicate a permanent delivery failure and should be removed from the email list immediately.
General Bounce
Sometimes, emails may bounce back due to reasons other than soft or hard bounces. These are classified as general bounces and may require further investigation to determine the underlying cause.
General bounces may include issues such as temporary server outages, network connectivity problems, or other technical issues preventing the email from being delivered successfully. These bounces often require further investigation to determine the specific cause and resolution.
Hard Bounce vs. Soft Bounce
Understanding the difference between hard and soft bounces is essential for devising an appropriate action plan.
While soft bounces are often temporary and resolved on their own, hard bounces require proactive measures to ensure successful email delivery.
Soft Bounce
A soft bounce means that the Email was valid and reached its recipient but was bounced back due to temporary issues. These issues can sometimes be fixed by simply waiting and sending the Email later or by checking the size of the email you sent. If you encounter a soft bounce, try again later, and the Email will most likely go through once the problem is fixed on the receiver’s end.
Hard Bounce
On the other hand, a hard bounce is when an email is bounced back for permanent reasons. This is a more severe problem than a soft bounce.
This bounce generally happens immediately, as soon as you send the Email. Not all hard bounces can be fixed because some hard bounces happen if an email no longer exists, or a receiver has blocked your Email.
But some hard bounces can be fixed. It could be as simple as checking the email to ensure its spelled correctly, or the problem could be more complicated.
How to Calculate Email Bounce Rate?
Calculating your email bounce rate is crucial for maintaining a clean email list and ensuring successful email marketing campaigns.
To calculate the email bounce rate, you need to know two key metrics: the number of bounced emails and the total number of emails sent. Here’s how to do it:
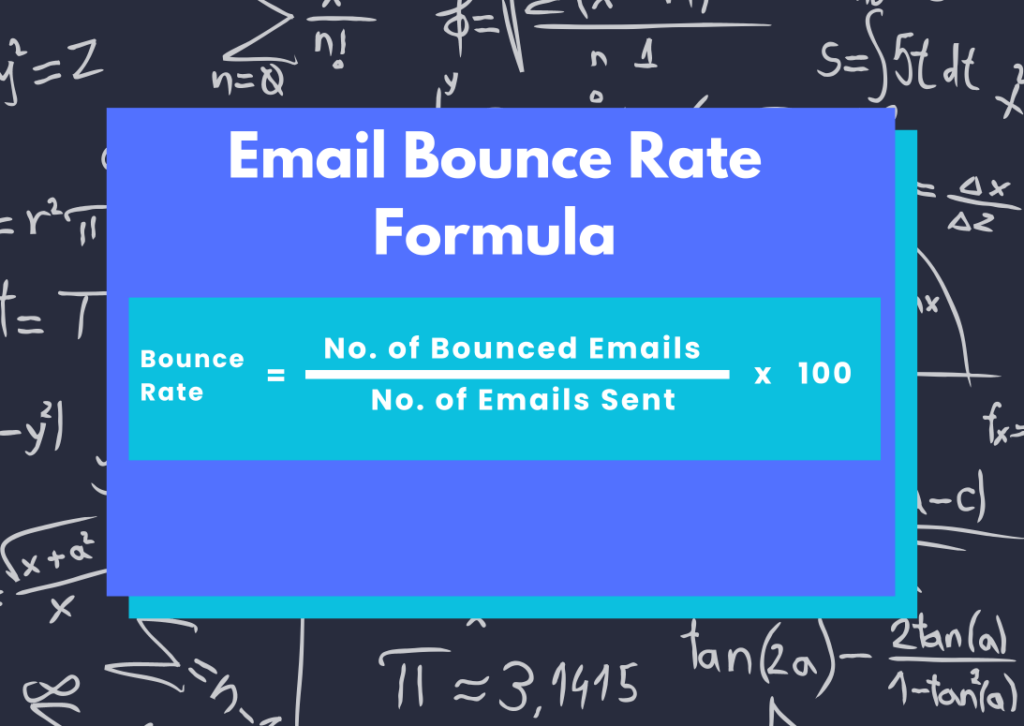
Formula:
Bounce Rate = (Number of Bounced Emails / Number of Emails Sent) x 100%
Example:
Let’s say you send 1,000 emails and receive 20 bounces.
Bounce Rate = (20 Bounced Emails / 1,000 Emails Sent) x 100% = 2%
What is an Acceptable Email Bounce Rate?
The lower the bounce-back rate, the better. A bounce-back rate of 2% or lower is the standard to aim for. This means less than two percent of your emails are bounced back to you.
You may find that bounce-back rates fluctuate with each email you send, which is normal. However, any drastic changes should be a red flag.
If your back bounce rate is anywhere from 2-4%, you should investigate why, and if it’s above 10%, you should take immediate steps to lower the back bounce rate.
Possible Reasons for Email Bounce Back
The best way to prevent email bounces back is by avoiding them altogether. Recognizing what causes them will help you know how to prevent them before they happen.
Emails may bounce back or be undelivered for various reasons, ranging from technical issues to recipient-related issues. Here are some possible reasons for email bounce back:
Invalid or Non-existent Email Address
One of the most common reasons for email bounce back is an invalid or non-existent email address. This occurs when the recipient’s email address is misspelled, contains typos, or does not exist.
Recipient’s Mailbox is Full
If the recipient’s mailbox is full and cannot accept any more emails, the email will bounce back. This typically results in a temporary bounce, and the email may be successfully delivered upon retry.
Server Issues or Downtime
Temporary issues with the recipient’s email server, such as server downtime, maintenance, or technical problems, can cause emails to bounce back. These issues may resolve themselves once the server is back online.
Blocked Sender
The recipient’s email server may block emails from specific senders or domains due to suspicions of spam, security concerns, or other reasons. If the sender’s domain or IP address is blocked, emails may bounce back consistently.
Invalid Domain Name
If the domain name in the email address is misspelled or does not exist, the email will bounce back. It’s essential to ensure the domain name is correct and properly formatted.
SPF/DKIM/DMARC Authentication Failure
SPF (Sender Policy Framework), DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail), and DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) are email authentication methods used to verify the sender’s identity and prevent email spoofing. If authentication fails, emails may bounce back.
Content Filtering
Some email servers use content filtering mechanisms to block emails containing certain types of content, such as spam, malware, or phishing attempts. If the email is flagged by content filters, it may bounce back.
Size Limit Exceeded
If the size of the email exceeds the recipient’s mailbox size limit or the email server’s size restrictions, it may bounce back.
Syntax Errors in Email Header
Syntax errors or formatting issues in the email header, such as missing or misplaced characters, can cause emails to bounce back.
DNS Configuration Issues
Problems with the Domain Name System (DNS) configuration, such as incorrect MX (Mail Exchange) records or DNS resolution issues, can prevent emails from being delivered.
Possible Reason for Soft Bounces (Temporary Failures)
- Full Inbox: The recipient’s inbox is temporarily full, but retrying later might succeed.
- Server Issues: The recipient’s mail server may be experiencing temporary downtime.
- Spam Filters: The recipient’s email provider might flag your email as spam, requiring adjustments to content or sending practices.
- Large Attachments: Files exceeding recipient server limits can bounce. Try compressing them or using cloud storage links.
- Auto-Responders: The recipient might be out of the office with an auto-reply triggered.
Soft bounce issues are frequently resolved by trying to send the Email again later.
Possible Reasons for Hard Bounces (Permanent Failures)
- Invalid Address: Typos, incorrect domains, or non-existent addresses lead to permanent delivery failure.
- Closed Account: The recipient’s email account may be closed or inactive.
- Mailbox Full: The recipient’s inbox has exceeded its storage limit.
- Domain Issues: Issues with the recipient’s mail server can prevent delivery.
- Spam Traps: Spam traps are fake email addresses used to identify spammers. Avoid buying email lists and practice permission-based marketing.
Some email domains like a government or an institution have spam filters on their emails that automatically block certain emails, or it is possible someone stopped your Email on purpose.
One of the best ways to avoid email bounce-back is by enabling double opt-in when a user signs up for an email list.
The user will enter their email address and then be emailed a link and must open it and confirm their Email.
This dramatically reduces the number of spam email addresses on your email list; thus, a bounce back before it happens.
How to Fix Email Bounce Back?
Fixing email bounce backs requires identifying and addressing the underlying cause of the delivery failure. Here are steps to fix email bounce backs:
Review Bounce Back Messages
Pay attention to the bounce back messages provided by your email server or service provider. These messages often contain valuable information about the reason for the bounce, such as invalid recipient address, server issues, or authentication failures.
Verify Recipient Email Addresses
Check the accuracy and validity of recipient email addresses. Ensure there are no typos or formatting errors and that the email addresses are active and correctly spelled.
Resend the Email
If the bounce back was due to a temporary issue such as a full mailbox or server downtime, consider resending the email after some time. The issue may resolve itself, and the email may be successfully delivered upon retry.
Update Sender Authentication
Ensure that your email-sending domain has proper SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records configured to authenticate the sender’s identity and prevent email spoofing. Address any authentication failures identified in bounce back messages.
Remove Invalid Email Addresses
Remove invalid or non-existent email addresses from your email list. Continuing to send emails to invalid addresses can harm your sender’s reputation and deliverability. Regularly clean and update your email list to maintain its accuracy.
Address Content Filtering Issues
Review the content of your emails and ensure they comply with content filtering guidelines. Avoid using spammy language, misleading subject lines, or content that triggers spam filters. Test different content variations to identify and address filtering issues.
Resolve Server or DNS Issues
If the bounce back was due to server or DNS configuration issues, work with your email service provider or IT team to resolve these issues. Ensure that your email server is properly configured, and DNS records are correctly set up to facilitate email delivery.
Contact Recipients
If the bounce back was due to specific recipient issues, such as a full mailbox or blocked sender, consider reaching out to the recipient to address the issue. Ask them to clear their mailbox, whitelist your email address, or report any delivery problems to their email administrator.
Monitor Bounce Rates
Continuously monitor your email bounce rates and investigate any significant spikes or patterns. Regular monitoring allows you to identify and address delivery issues promptly, improving overall email deliverability.
Final Words
Email can be a powerful tool for your business, but it can also be frustrating and quickly take up valuable time.
Email bounce backs are a common occurrence in email marketing, but they can be managed effectively with the right strategies in place.
Knowing how to analyze your email analytics—opens, clicks, unsubscribes, bounce back rates, etc. is the key to understanding how to decrease your bounce back rate.
The higher your email volume, the harder it is to handle. The best way to prevent email bounce back is to do things right the first time.
Bluedot Email is your all-in-one solution for anything related to email marketing. Let Bluedot Email handle your email marketing, so you have more time to focus on your business.
From assisting you in writing the perfect and compelling subject line to creating a personalized video email campaign and becoming an expert email marketer, Bluedot Email is ready to help you connect to your audience, convert emails to sales, and grow your business.
